Pregnancy comes with a flurry of changes, and how much weight to gain remains a common question. Discover why gaining the right amount is so essential for a healthy birth and beyond.
A new pregnancy is filled with excitement and anticipation, but there is also no shortage of worries that seem to come all at once: are my favorite foods still okay to eat? My body is changing by the day - how will I cope? And how do I know how many pounds to put on? A growing baby, placenta, amniotic fluid, increased blood volume, and fat stores all contribute to a steady increase in weight over time. Gaining the right amount – not too much and not too little – over the course of your pregnancy is key for preventing complications for you and your baby.
How much should I gain during my pregnancy?
How much you should gain will mostly depend on your pre-pregnancy BMI. The lower your BMI, the more weight gain you should aim for:
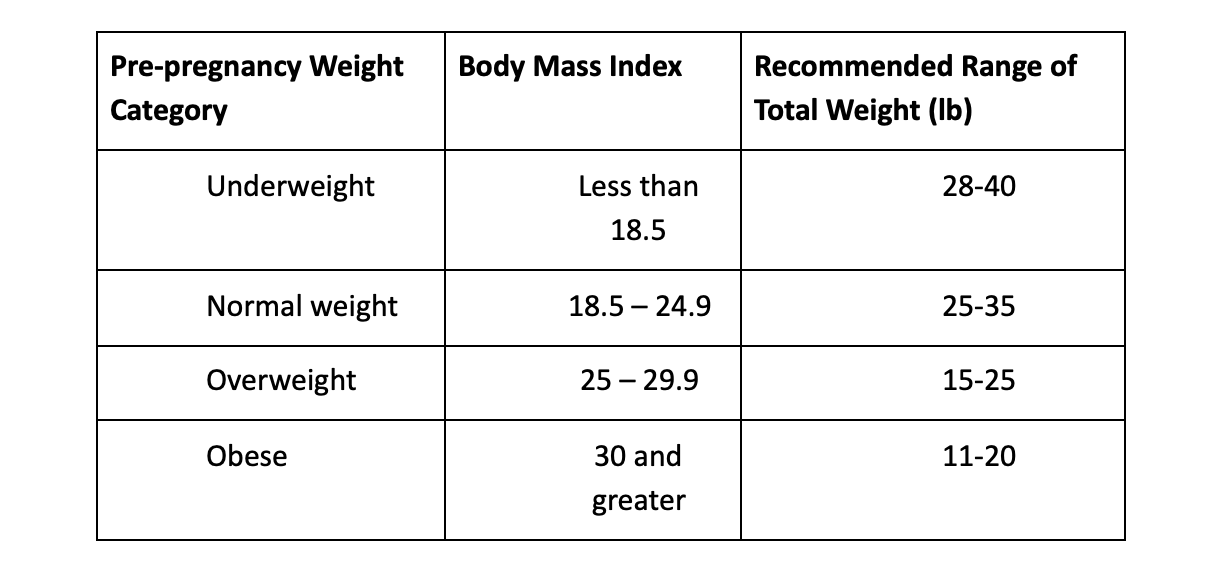
Most women will gain only 1.1 to 4.4 lb during the first trimester regardless of BMI. During the second and third trimesters, underweight and normal weight women should gain 1 lb per week, overweight women should gain 0.6 lb per week, and obese women should gain 0.5 lb per week.
Why is it so important to maintain a healthy weight during pregnancy?
Too much or too little weight gain during pregnancy can have lifelong effects for both you and your baby. Women who gain too much increase their likelihood of complications like high blood pressure during pregnancy, a c-section birth, and a baby who is large at birth and prone to being overweight or obese during childhood. Plus, it is tougher to lose the weight after birth if you gained too much. Gaining too little weight is not safe either. Inadequate weight gain is linked to giving birth too early and to a baby who is small and at higher risk for illness and developmental delays. For these reasons, it is important to work with your doctor to stay on track with your weight throughout your pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes: what it is and how to manage it
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that can develop during pregnancy and is usually diagnosed between 24-28 weeks. It affects nearly 1 in 10 pregnant women. Gestational diabetes results when the mother’s insulin is not able to process the sugar in her bloodstream very well, resulting in extra sugar collected in the blood. Experts do not really know the exact cause of this condition, and for most women, it resolves soon after the pregnancy. If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, it is important to know that it is treatable and manageable. It is very much possible to have a healthy pregnancy and healthy baby. With your doctor’s help, you can learn how to successfully keep normal blood sugar levels by exercising regularly, following a healthy eating plan, and in some cases, taking insulin.

Tips for managing a healthy weight during pregnancy
Slimming down should never be the goal while pregnant, and “eating for two” does not mean you should be careless about what and how much you are eating. Making your regular prenatal appointments, eating healthy foods, and being active every day will ensure you are gaining the amount that you need. Every little bit helps and the earlier you start making healthy changes, the better:
Make healthy food choices. Keep eating healthy easy by stashing wholesome foods within reach at home. Eat lots of fruits and vegetables during meals and for snacking. Stick to whole grain cereal, breads, and crackers, and low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese. Cut down on calories by avoiding greasy, fried foods and junk foods like ice cream, chips, candy, and cookies.
Get some exercise every day. Ask your doctor about exercise activities that are safe for you. Walking, swimming, yoga, and strength training are usually considered safe for pregnancy.





